How To Determine Whether Crane Parts Need To Change
Cranes are essential equipment in various industries, from construction to manufacturing. They consist of numerous components that work together to facilitate heavy lifting and movement. However, like any mechanical system, crane parts can wear out over time due to extensive use and environmental factors. It is crucial to assess the condition of these parts regularly to ensure safe and efficient operation. This article will guide you on how to determine whether crane parts need to be changed.
End-of-life Criteria For Main Beams
The crane has been overhauled several times, and the main girder is severely deflected or cracked several times after two deflections have been repaired, which marks the end of its safe service life.
A qualified bridge crane’s main beam deflection deformation and cracks belong to fatigue damage, which is the material organization structure in the stress under the action of local cyclic slip and yielding and the gradual formation of linear cumulative damage. Therefore, repeated serious downward deflection or repeated cracks mark the end of the safe service life of the main girder.
In general, the safe service life of grab cranes and electromagnetic cranes is 20 years, casting cranes are more than 30 years, and general-purpose bridge cranes are 40 to 50 years. The actual service life of the crane is determined by the specific conditions of use, not necessarily in line with the above years.

End-of-life Criteria For Hook
Hooks with the following defects shall be scrapped and replaced:
- Cracks
- Dangerous section wear exceeding 10% of the original height
- Dangerous section and hook neck produce plastic deformation
- Opening increased by 15% from the original size
- Torsional deformation of the hook tip exceeding 10 degrees or more
- When the wear of the plate hook bushing reaches 50% of the thickness, the bushing should be scrapped
- If the wear of the mandrel of the plate hook reaches 5% of the original size, the mandrel should be scrapped
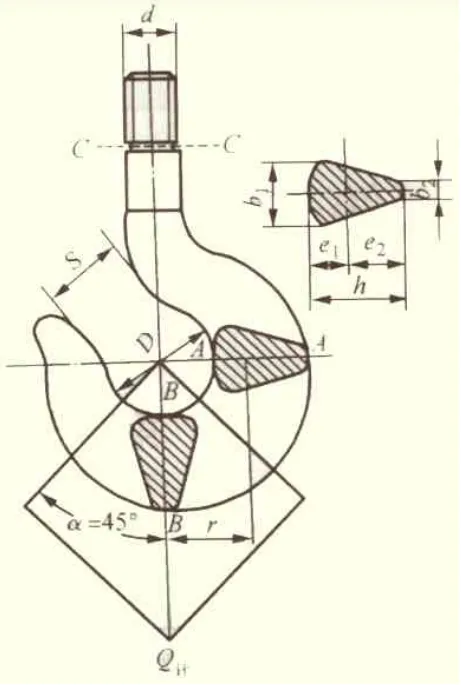
Hazardous Section Of The Hook:
The dangerous section of the hook is an important part of the daily inspection and safety inspection, after analyzing the force of the hook, it is concluded that the hook has the following dangerous sections.
- B-B section: This section has shear stress, and at the same time, this section is often worn, so that the cross-sectional area is reduced
- Section C-C: This is the smallest section and there is a danger of being pulled off
- Section A-A: This section is subjected to complex forces
End-of-life Criteria For Sheaves
Sheaves shall be scrapped and replaced if they have the following defects:
- The wall thickness of the rope groove of the sheave is worn up to 20% of the original thickness
- The radial wear at the bottom of the rope groove of the sheave exceeds 50% of the diameter of the wire rope or the uneven wear exceeds 3mm
- Cast iron sheave found more serious cracks
- Serious damage to the sheave rim
- Cracks
- Other defects that damage the wire rope

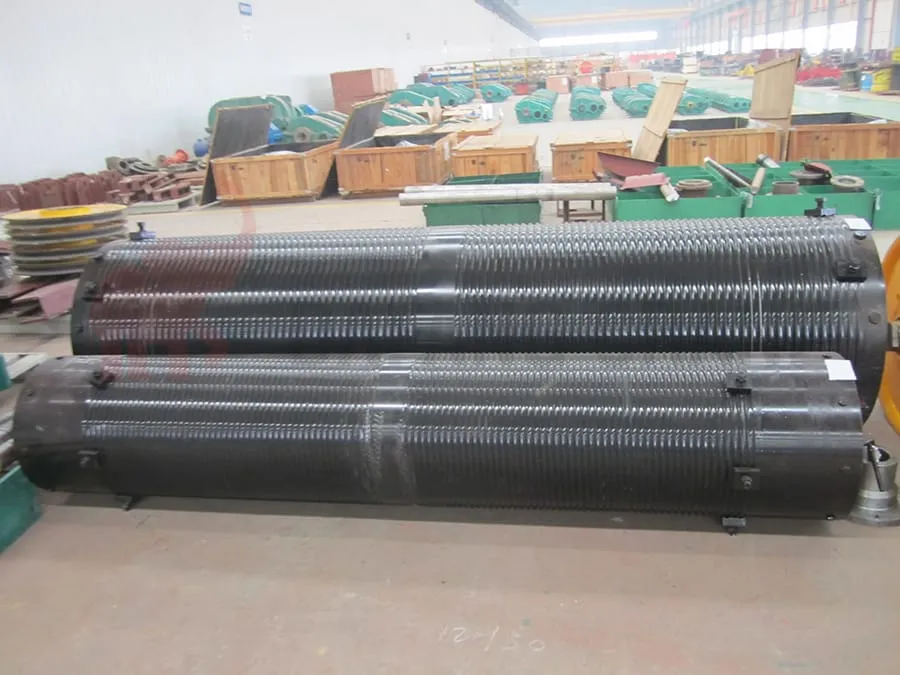
End-of-life Criteria For Drums
When one of the following conditions occurs in a drum, it shall be scrapped:
- When the wear of the drum wall reaches 20% of the original wall thickness, the drum should be scrapped.
- Check the drum and shaft shall not have cracks, if cracks are found, they should be scrapped and renewed in time.

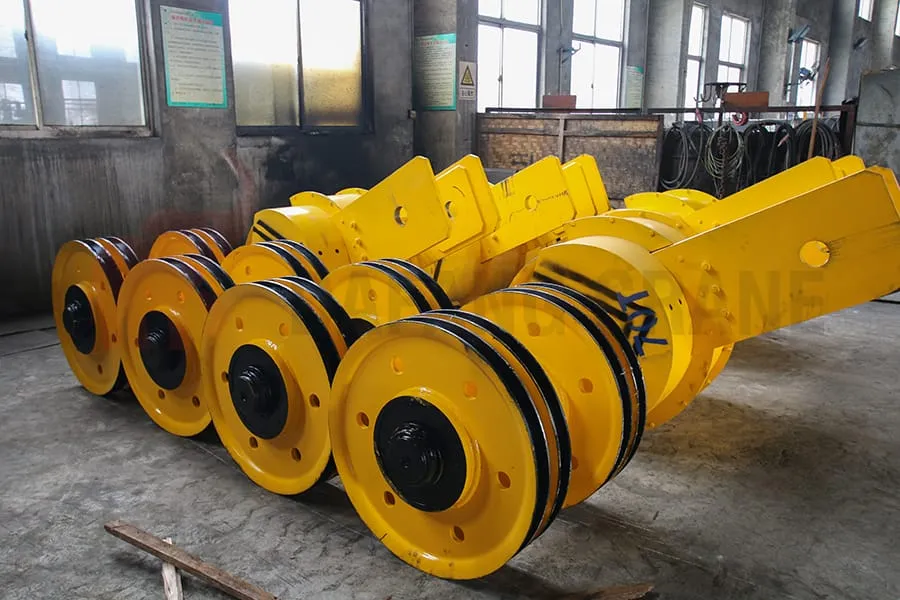
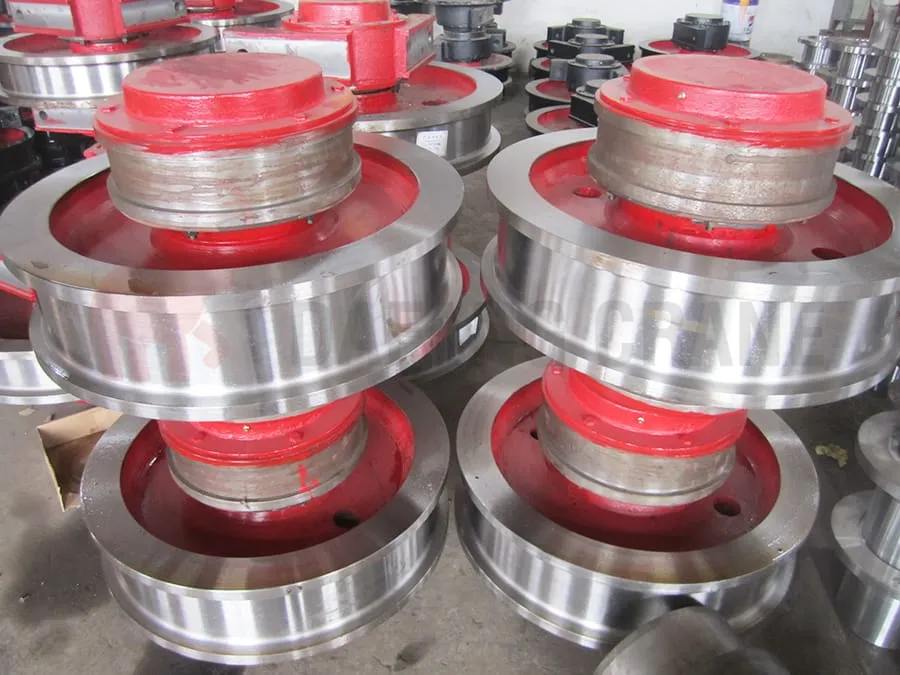
End-of-life Criteria For Wheels
Wheels should be scrapped when one of the following conditions occurs:
- Cracks
- When the running speed is lower than 50m/min, the degree of ellipticity (ellipticity=maximum diameter-minimum diameter) reaches 1mm, and when the running speed is higher than 50m/min, the degree of ellipticity reaches 0.5mm, it should be scrapped and replaced.
- If the thickness of the tread of the wheel is worn to 15% of the original thickness, it should be scrapped and replaced.
- If the wear of the wheel rim exceeds 50% of the original thickness, it should be scrapped and replaced.

End-of-life Criteria For Brakes
If the brake has the following defects, it should be scrapped and replaced:
- Wear of the brake pads exceeds 50% of the original thickness.
- The wear of the minor shaft and mandrel exceeds 5% of the original diameter.
- Fatigue cracks on tie rods, brake arms, and springs.
- Excessive heat or damage to the rolling bearings of the hydraulic actuator brake.
- Cracks
- Plastic deformation(irrecoverable deformation) of springs
End-of-life Criteria For Brake Wheels
Brake wheels shall be scrapped if any of the following conditions occur:
- Cracks
- If there are defects and cracks on the work surface of the brake wheel, it should be scrapped and replaced.
- The brake wheel of the hoisting mechanism shall be scrapped when the wear exceeds 40% of the original thickness, and the brake wheel of the running mechanism shall be scrapped and replaced when the wear exceeds 60% of the original thickness.
Wire Rope Scrap Criteria
The wire rope shall be scrapped and replaced if one of the following conditions occurs:
- Wire rope in a pitch (wire rope strands around the axial distance) within the number of broken wires up to 10% of the total number of wires of the rope
- Wire rope wear, diameter reduction, if more than 40% of the diameter of the wire rope, should be scrapped and replaced
- The whole strand of the wire rope breaks or the core of the wire rope is extruded, resulting in structural damage to the wire rope.
- Wire ropes with significant internal corrosion.
- Serious deformation of wire rope such as kinking, dead ends, hard bends, plastic deformation, etc.
- When the safety factor is less than 6, the renewal standard is to break the number of wires in a twist distance up to 10% of the total number of wires of the wire rope. If it is 6*9=114 wires, when the number of broken wires reaches 12 wires, it can be scrapped and renewed, 6*37=222 wires, when the number of broken wires reaches 22 wires, it can be scrapped and renewed. When the safety factor is 6~7, the number of broken wires is 12%, and when the safety factor is more than 7, the number of broken wires is 14%.
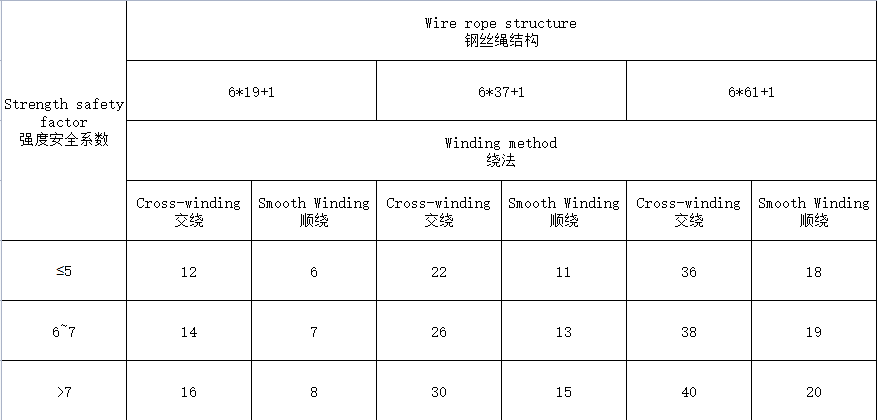
Table 1: Steel wire rope broken wire scrapping standard
- If the outer layer of the wire has serious wear, but is less than 40% of the diameter of the wire rope, it should be based on the degree of wear, the number of broken wires shown in Table 1 for scrapping should be discounted according to Table 2, and scrapped according to the number of broken wires after discounting.
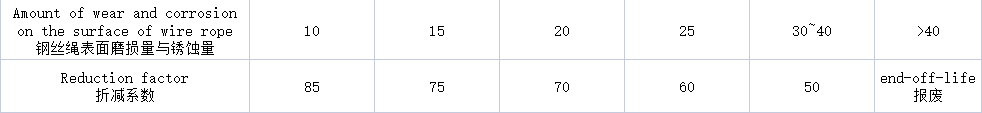
Table 2: Steel wire rope discount coefficient table
Example: 6 * 37 + 1 cross-wound wire rope, safety factor of 5, the surface wear of the wire rope for 25%, then a twisting distance within the broken 22 * 60% = 13.2 steel wire scrapped.
Ensuring the safety and efficiency of crane operations necessitates regular assessment of crane parts for replacement. Henan Dafang Heavy Machinery Co., Ltd. is a crane manufacturer with perfect testing equipment and advanced production equipment as well as a professional technical research and development team. Manufacture of crane hooks, crane wheels, sheaves, crane rope drum, grab, trolley, winch and many other crane accessories. If you have any questions or needs about cranes and crane parts, please contact us!

